When people talk about AI chatbots in 2026, they often jump straight to models and tools. In reality, what matters far more is how the chatbot fits into real business workflows.
The best chatbots of today are not rule-based scripts. They’re smart systems that really understand what the user is after, handle multi-step conversations with ease, and work well with both the customer and the people they’re working alongside. When done right, they answer the same old routine questions that everyone asks, automate time-consuming tasks, give your support team some breathing room, and help you actually learn something from the conversations you have.
Table of Contents
Common Types of AI Chatbots Used in Business
Most chatbots are shaped by the role they play, not the technology behind them. While many production systems eventually blend multiple functions, strong implementations usually start with one clear purpose and expand from there.
Support and FAQ Bots
These are the ones people usually start with. They deal with all the repetitive questions people always ask, give customers the answers right away, and help take some of the pressure off the customer support crew. When done well, they don’t replace humans; they protect them from burnout by filtering out low-value interactions.
Agent-assist Chatbots
Rather than talking to customers directly, these chatbots just sit alongside human agents, flashing up any relevant information, suggesting responses or recommending what to do next in real-time. We’ve seen these dramatically improve response speed and consistency, especially in high-volume contact centers.
The Transactional Bots
Transactional chatbots are action-oriented. They track orders, book appointments, update accounts, or check on the status of things by actually connecting directly to the business systems they need to. Their value is all about making things happen: fewer clicks, fewer issues and way less manual work in the background.
Internal Chatbots
These are the ones that help employees get around internal systems and documentation without having to dig around or ask around. They often get overlooked, but in practice, they reduce all that friction between departments and make it way easier to get your hands on the information you need.
Choosing a Chatbot Creation Strategy that Succeeds
What’s key in chatbot development isn’t the tech you use or where you host it. It’s figuring out what’s in scope: what your chatbot is supposed to actually do. Too often, teams try to build a chatbot that’s a jack of all trades, and that usually ends up in frustratingly unclear behavior and dodgy results. The better approach is to hone in on one or two things your chatbot can actually solve and be clear on when it should wing it on its own versus handing off to a human.
Examples of chatbots with a clear purpose:
- Answering people’s most frequently asked website questions.
- Helping users track their orders.
- Supporting employees with the internal knowledge they need to do their jobs.
- Filtering out incoming leads before they even reach support or sales teams.
Keeping things focused makes the chatbot much easier to launch, test and improve, plus you get useful data right out of the gate.
Key Things to Consider for Reliable, Secure and User-Friendly Chatbots
You don’t have to build a super advanced chatbot to deliver real value. Even simple ones need to strike a balance between doing things right, being secure, integrating well and making users happy:
- Execution: Get clear on what your chatbot can do, map out all the different questions it should be able to handle and think about all the times it will probably go wrong. Then plan for how it will escalate to a human when it’s not sure.
- Integration: Make sure your chatbot connects to all the right systems – your CRM, your ERP, APIs and all the other tools your business uses. So it can do things like update records or trigger workflows.
- Security: From the very start, make sure your chatbot is secure. Think about stuff like privacy, encryption and monitoring. Limit access to what’s absolutely necessary, and do some careful logging and keep a clear record of everything that happens.
- User Experience & Brand Alignment: Think about how the user will interact with your chatbot. Map out what happens if it can’t understand what they mean, and make sure your responses sound friendly, predictable and in line with your brand. Keep inputs and flows clear and guided, so users don’t get confused.
By getting these pillars in place upfront, you set up your chatbot for success – it feels trustworthy, does its job well and integrates seamlessly with your business.
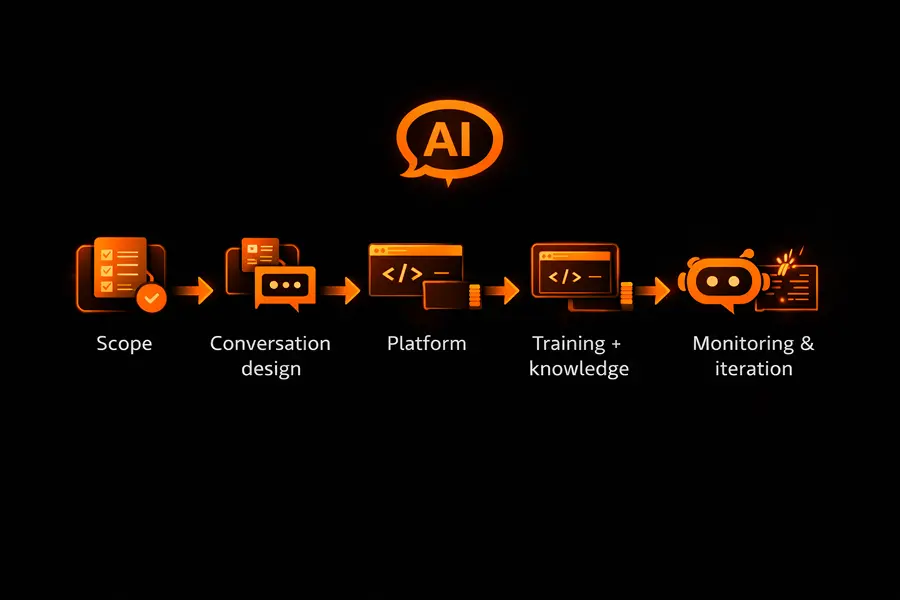
Step-by-Step: How AI Chatbot Development Works in Practice
Step 1: Define Scope and Handoff Rules
Start by clearly specifying what the chatbot should handle and what should be passed to human agents. Map supported intents and edge cases to avoid guessing and reduce errors. This scope defines when the bot can act independently and when it should escalate, for example:
- Answering FAQs
- Helping users track orders
- Supporting employees with internal information
- Filtering leads before they reach human agents
Keeping the scope tight makes the chatbot easier to launch, test, and refine while producing actionable usage data early.
Step 2: Design Conversation Flows
Plan how conversations should unfold. Identify common user inputs, alternative phrasings, and fallback paths when the chatbot does not understand. Include clarification loops and multi-step tasks to guide users toward completion.
Users rarely communicate in predictable ways. They may skip context, rephrase, or change direction mid-conversation. Designing flows upfront helps the chatbot handle ambiguity without frustrating users. Simple diagrams or conversation design tools make it easier to visualize paths, spot gaps, and fix weak points before development. Well-structured flows also ensure consistent and natural responses across websites, messaging apps, and mobile platforms.
Step 3: Choose Platform and Tools
Select tools based on your chatbot’s complexity, integration requirements, and scalability. Popular platforms include Dialogflow, Microsoft Bot Framework, IBM Watson Assistant, and Rasa, each offering features like NLP, multi-channel deployment, and enterprise-grade integrations.
| Tool / Platform | Core Focus | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Dialogflow | NLP, intent detection | FAQs, customer support, messaging bots |
| Microsoft Bot Framework | Enterprise orchestration | Multi-channel, real-time assistance |
| IBM Watson Assistant | NLP, sentiment analysis | Support bots, knowledge-based assistants |
| Rasa | Open-source, full control | Complex workflows, enterprise use cases |
| Amazon Lex | Text and voice NLP | Voice-enabled assistants |
| Python (custom development) | Full customization | Scalable, tailored chatbot systems |
| Chatfuel / ManyChat | No-code, rule-based | Simple marketing bots, basic FAQs |
Python is widely used because it’s simple to read, easy to use, and has a vast array of libraries that support advanced NLP and machine learning. No-code tools like Chatfuel and ManyChat are okay for simple FAQs or marketing bots, but they don’t have the advanced features you need for enterprise-scale apps.
The platform you choose has a big impact on performance, scalability, and how much business logic the chatbot can handle. Using the right platform and some good frameworks can help your AI chatbot understand what the user wants, learn from past conversations, and give personalized responses over time.
Step 4: Train the Model and Feed it Some Knowledge
Training the model is what makes it reliable and can contextually answer questions. Give the model some domain-specific data, like support tickets, past conversations, product documentation, and internal knowledge bases.
Then connect the chatbot to a knowledge base, so that it can pull up accurate, real-time information from trusted sources instead of just making stuff up. Most production chatbots use a combination of NLP or big language models with Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). Rather than relying solely on the model, the chatbot goes and gets verified information from internal sources to shape each response. This reduces the chances of the chatbot just making stuff up, which improves accuracy and lets you update the knowledge base without having to retrain the entire model from scratch.
It is important to remember that training is an ongoing process: reviewing logs, monitoring failed interactions, and testing edge cases helps the chatbot learn from real conversations, improve its ability to understand what the user is asking, and get better at giving accurate, relevant responses. Ongoing monitoring and maintenance of the chatbot’s knowledge base and workflows make sure it stays accurate, relevant and performant over time.
Step 5: Get the Chatbot Talking to Your Business Systems
Connect up the chatbot to your CRM, ticketing system, ERP, and APIs so that conversations get turned into real action, like updating orders, creating tickets or getting customer data. Integrations can be straightforward, or they might involve using automation tools, but they’re what make a conversation into something with real value. Without system access, even the most advanced AI chatbot is basically just stuck doing informational tasks.
Step 6: Test, Monitor, and Keep Improving
Before you launch, run some thorough testing to make sure the chatbot doesn’t just fall over. Include some unexpected and just plain weird inputs to make sure it’s solid.
After you launch, keep a close eye on performance metrics and KPIs like resolution rate, user satisfaction and conversation success. Use feedback loops, review conversation logs and refine flows to keep the chatbot reliable. Treat the chatbot as a living product, iterating to handle new use cases, integrations and user behaviors while keeping performance consistent.
Learning and Building AI Chatbots Without Extensive Coding
Creating AI chatbots no longer requires deep programming expertise. Today, a combination of educational resources, low-code/no-code platforms, and hands-on experimentation makes it possible for beginners to design functional, intelligent chatbots that integrate into real workflows.
Educational Resources and Guided Codelabs
For those just starting out, structured learning paths are invaluable. Google’s Agent Development Kit (ADK) offers a hands-on codelab series where users can build AI agents step by step, learning how to manage conversation flows, integrate basic logic, and connect to services.
Similarly, platforms like Coursera provide beginner-friendly courses, such as “Building AI-Powered Chatbots Without Programming”, which focus on practical skills rather than theory. These resources help learners understand the fundamentals of chatbot design, natural language processing, and multi-step conversation handling, all without requiring advanced coding knowledge.
Low-Code and No-Code Platforms
For those who want to bring ideas to life quickly, low-code platforms offer a flexible way to build AI chatbots with minimal programming. Teams can visually assemble conversation flows, implement business logic, and connect to existing systems without writing complex code.
No-code tools take accessibility even further. Solutions like Botpress and Zapier Chatbots allow anyone to launch fully functional AI chatbots using drag-and-drop interfaces, prebuilt workflows, and ready-made integrations. While these tools are ideal for simple FAQs, marketing bots, or internal assistants, they also provide a gateway for experimentation and learning before scaling to more complex implementations.
Testing and Iteration in Real-World Conditions
Testing is where chatbot assumptions meet real user behavior. People rarely follow clean, predictable conversation paths, so early versions must be tested against unclear, incomplete, and unexpected inputs. This is how you verify that the chatbot understands intent correctly, handles edge cases, and fails safely when it should escalate or ask clarifying questions.
Training quality plays a major role here. Using relevant, domain-specific datasets improves intent recognition, response accuracy, and consistency. Many teams also introduce multilingual support at this stage to make the chatbot usable across different markets and user groups.
Continuous improvement depends on feedback loops. Reviewing conversation logs, tracking failed interactions, and collecting lightweight user feedback (for example, short surveys or thumbs-up/down signals) helps identify where responses break down. These insights are then used to refine conversational flows, update knowledge sources, and improve performance over time.
Cost and Time to Market
The cost of building an AI chatbot goes far beyond the language model itself. Teams need to account for data preparation, conversation design, system integrations, security controls, and ongoing optimization. Each of these factors influences both development effort and long-term maintenance.
From a timeline perspective, a basic prototype can often be launched within a few weeks. However, turning that prototype into a production-ready chatbot that integrates with business systems, supports scale, and meets compliance requirements typically takes two to four months. Planning for this upfront helps avoid rushed launches and costly rework later.
In-House, Using an Agency, or Hiring Freelancers: Choosing the Right Approach
When planning to create a chatbot, deciding who builds it will impact cost, speed, scalability, and how easily you can maintain and improve its performance over time. Depending on your target audience, the complex tasks your bot needs to handle, and your digital channels, you have three main options:
Building Chatbots Internally
For teams with existing artificial intelligence or machine learning expertise, developing a chatbot in-house gives total control over its conversational flows, integrations, and human-like responses. You can customize the bot to match your customer experience goals, connect it to your database, and implement data security measures directly.
Internal development allows teams to gather feedback, iterate quickly on a draft version, and integrate with multiple software modules or frontend displays. It’s ideal for organizations that need more advanced bots, personalized experiences, and real business value. The downside is the upfront effort required to set up the essential tools, configure systems, and train the bot on human language nuances.
Working with Freelancers
Freelancers can help you get started fast, especially for prototypes, rule-based chatbots, or simple workflows that answer common questions. They are useful for generating quick answers, handling FAQs, or testing dialogues before wider deployment.
However, if your project grows in scope (handling multiple channels, complex tasks, or integrating databases and APIs) freelancers may struggle without clear documentation or structured feedback loops. This approach works best when you’re exploring just the beginning of your chatbot journey or need a short-term solution to improve customer experiences.
Partnering with an AI Chatbot Development Agency
Agencies offer a proven approach to deploy AI bots that scale across WhatsApp, web, and other digital channels. They bring experience in generative AI, human conversation design, and analytics, ensuring the bot delivers real business value while maintaining data security and clarity in responses.
A good agency can help you learn how to create chatbots that handle complex tasks, answer questions, collect contact details, and personalize experiences for your audience. They also support iterative improvement, allowing you to share feedback, improve performance, and adapt the bot as your organization’s specific needs evolve.
Choosing the right approach depends on your budget, timeline, technical skills, and long-term customer engagement goals. Regardless of the path, testing, feedback, and continuous improvement are essential to improve customer experiences, generate productivity, and ensure your AI chatbot is more than just a feature; it’s a living digital asset.
Turning Chatbot Development Into a Long-Term Asset
A chatbot only creates value if it’s treated as part of your product, not a one-off feature. When it’s built with clear goals, connected to real systems, and improved over time, it can reduce manual work and support day-to-day operations in a meaningful way.
That means launching AI tools with a focused scope, watching how people actually use them, and adjusting flows and logic based on real conversations.
ProductCrafters’ developers work with companies to design and scale AI chatbots that fit real business workflows and stay reliable at scale. Learn more about working together with ProductCrafters.